Pull-up (negative) (male) – Video Exercise Guide & Tips
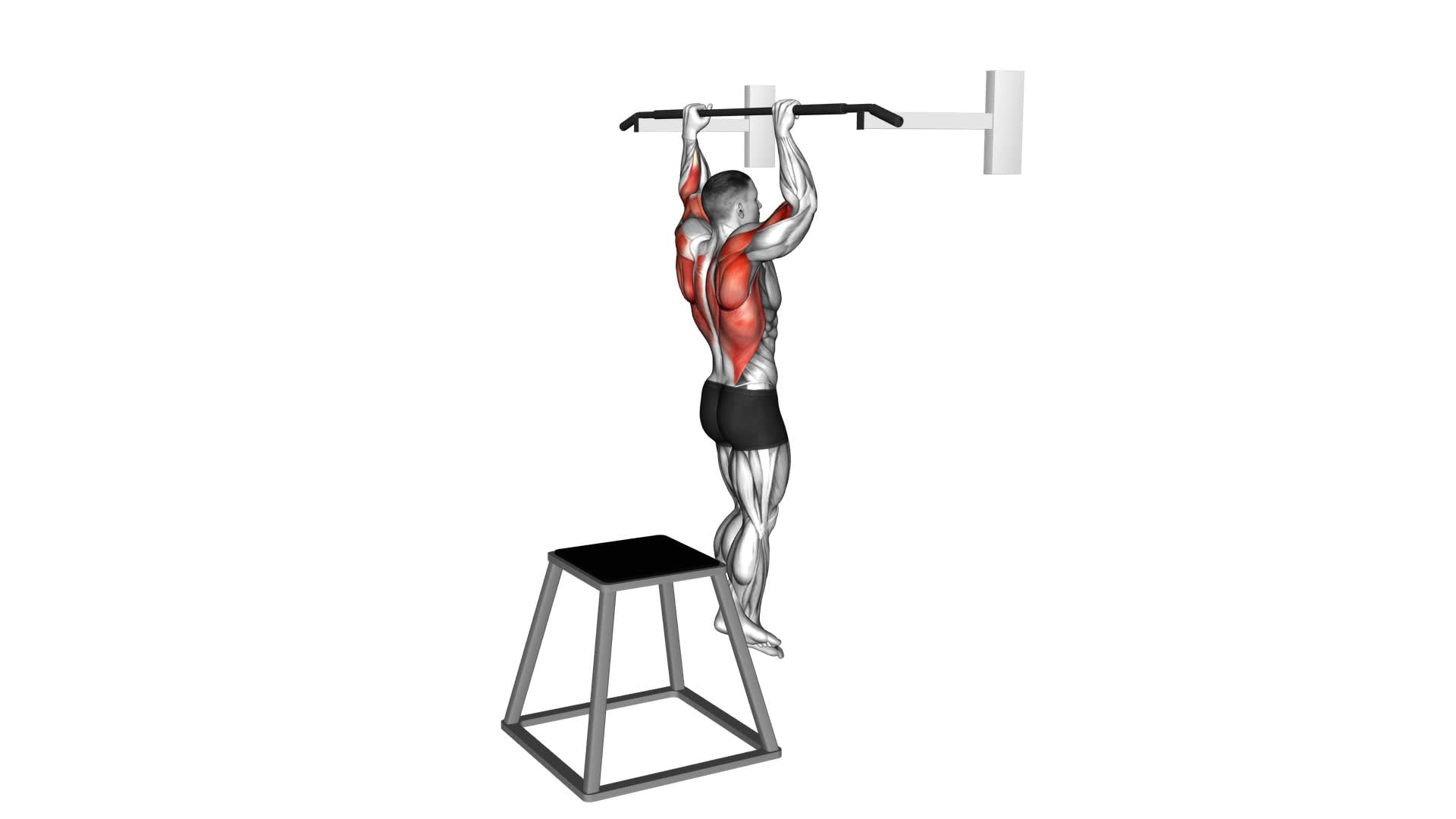
Looking to strengthen your upper body? Check out this video exercise guide for the pull-up (negative) specifically designed for male athletes.
Watch This Exercise Video
Learn the proper form and technique, as well as variations and progressions to challenge yourself. Avoid common mistakes and discover how to incorporate this exercise into your training routine.
Get ready to increase your strength and endurance with these helpful tips.
Let's get started!
Key Takeaways
- Pull-up (negative) targets muscles in the back, shoulders, and arms.
- Pull-up (negative) increases upper body strength and endurance.
- Pull-up (negative) engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
- Pull-up (negative) builds strength and muscle definition.
Benefits of Pull-up (negative) for Male Athletes
You can experience several benefits from incorporating pull-up (negative) exercises into your training routine as a male athlete. Pull-ups (negative) are a challenging exercise that primarily targets the muscles in your back, shoulders, and arms. By regularly including this exercise in your workout, you can significantly increase your upper body strength and endurance.
One of the main benefits of pull-ups (negative) is that they help to improve your overall muscular strength. This exercise engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, including your lats, biceps, and deltoids. As you pull yourself up, you're effectively working against gravity, which helps to build strength and muscle definition.
Additionally, pull-ups (negative) are an excellent exercise for improving your upper body endurance. By performing multiple repetitions, you're training your muscles to work for longer periods without fatigue. This increased endurance can be beneficial for various sports and physical activities, allowing you to perform better for longer durations.
To maximize the benefits of pull-ups (negative), it's essential to focus on proper form and technique. Start by using an overhand grip with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Engage your core muscles and pull your body up until your chin is above the bar. Control your descent as you slowly lower yourself back down.
Incorporating pull-ups (negative) into your training routine can provide numerous benefits for male athletes, including increased strength and endurance. By following proper form and technique, you can make the most out of this exercise and enhance your overall athletic performance.
Proper Form and Technique for Pull-up (negative)
To perform a pull-up (negative) with proper form and technique, start by gripping the bar with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Here are some key tips to help you execute this exercise correctly:
- Keep your core engaged and your body straight throughout the movement.
- Begin the exercise by slowly lowering yourself down, controlling the descent.
- Aim to lower yourself until your arms are fully extended, and your shoulders are in a relaxed position.
- Maintain a slow and controlled movement, focusing on the lowering phase rather than pulling yourself up.
- Breathe steadily throughout the exercise, exhaling as you lower yourself down.
- Ensure that your elbows are fully extended at the bottom of the movement.
- Avoid swinging or using momentum to complete the exercise.
By performing pull-up negatives with proper form and technique, you can effectively target your back muscles and build strength. Additionally, incorporating eccentric training, such as pull-up negatives, into your workout routine can offer several benefits, including increased muscle hypertrophy, enhanced joint stability, and improved muscular control.
Now that you understand the proper form and technique for pull-up negatives, let's move on to the next section to explore variations and progressions for advanced male lifters.
Variations and Progressions for Advanced Male Lifters
Explore advanced variations and progressions to challenge and further develop your pull-up (negative) exercise. As an advanced male lifter, it's important to incorporate advanced lifting techniques and effective muscle building strategies into your workout routine. By doing so, you can continue to push your limits and achieve new levels of strength and muscular development.
One variation to consider is the weighted pull-up (negative). This involves adding weight to your body using a weight belt or a weighted vest while performing the negative phase of the exercise. This added resistance increases the intensity of the exercise and stimulates further muscle growth.
Another progression is the one-arm pull-up (negative). This advanced variation requires exceptional upper body strength and stability. Start by performing negatives with one arm while holding onto a towel or using an assisted pull-up machine. As your strength improves, gradually decrease the assistance or switch to a regular pull-up bar.
To further challenge yourself, you can also try explosive pull-ups (negative). This involves rapidly pulling yourself up and then controlling the descent in a slow and controlled manner. This variation improves power and explosiveness, making it a great addition to your advanced training routine.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Pull-Up (Negative)
Continuing the discussion from the previous subtopic, it's important to be mindful of common mistakes to avoid during the pull-up (negative) exercise. To help you improve your form and get the most out of this exercise, here are some tips for avoiding these common mistakes:
- Swinging too much: One of the most common mistakes is swinging your body excessively during the negative phase of the pull-up. This not only reduces the effectiveness of the exercise but also puts unnecessary strain on your shoulders and lower back. Keep your body still and focus on controlled movements.
- Not engaging your core: Neglecting to engage your core during the pull-up (negative) can lead to poor form and decreased stability. Make sure to tighten your abs and glutes throughout the exercise to maintain proper alignment and support your bodyweight.
By being aware of these common mistakes and implementing these tips for improvement, you can enhance the effectiveness of your pull-up (negative) exercise.
Now, let's transition into the next section to learn how to incorporate pull-up (negative) into your training routine.
How to Incorporate Pull-Up (Negative) Into Your Training Routine
To incorporate the pull-up (negative) into your training routine, there are a few key points to consider.
First, understand the benefits of negatives, such as increased strength and muscle development.
Next, focus on progression and variations to challenge yourself and continue making progress.
Lastly, ensure you're using proper form and technique to maximize the effectiveness of the exercise and prevent injury.
Benefits of Negatives
To maximize your training routine, incorporate pull-up negatives for an effective upper body workout. Negatives, also known as eccentric training, offer several benefits that can enhance your overall strength and muscle development.
When performing negatives, you focus on the lowering phase of the exercise, which requires controlled muscle activation. Here are the key benefits of incorporating negatives into your training routine:
- Enhanced muscle activation: Negatives engage your muscles in a different way, activating more muscle fibers and leading to greater strength gains.
- Increased muscle growth: Eccentric training stimulates muscle hypertrophy, promoting muscle growth and development.
- Improved muscle control: By emphasizing the eccentric phase, negatives improve your control and stability during pull-ups, leading to better overall performance.
Incorporating pull-up negatives into your training routine can help you achieve better results and take your upper body strength to new heights.
Progression and Variations
How can you progress and incorporate pull-up negatives into your training routine to further enhance your upper body strength and muscle development?
There are several pull-up (negative) modifications and exercises for building upper body strength that you can try.
One option is to use resistance bands to assist you in performing the pull-up negatives. This can help reduce the amount of bodyweight you need to lift, making it easier to execute the exercise.
Another variation is the wide-grip pull-up negative, which targets your lats and improves overall upper body strength.
Additionally, you can incorporate isometric holds during the negative portion of the exercise to further challenge your muscles.
By incorporating these pull-up (negative) modifications into your routine, you can continue to progress and improve your upper body strength.
Now let's move on to the next section about proper form and technique.
Proper Form and Technique
To incorporate pull-up negatives into your training routine, focus on maintaining proper form and technique. This won't only maximize the effectiveness of the exercise but also reduce the risk of injury. Here are some common mistakes to avoid and tips to ensure you're performing pull-up negatives correctly:
- Keep your body straight and avoid swinging or using momentum.
- Engage your core and squeeze your shoulder blades together as you lower yourself down.
- Control the descent and aim for a slow and controlled movement.
- Avoid shrugging your shoulders or hunching your back.
- Use a grip that's comfortable for you, whether it's overhand or underhand.
By following these guidelines, you can incorporate pull-up negatives into your training routine safely and effectively.
Don't rush the process, focus on maintaining proper form, and gradually increase the difficulty as you progress.
Tips for Increasing Strength and Endurance in Pull-up (negative)
To increase your strength and endurance in Pull-up (negative), focus on proper form and controlled movements. This exercise primarily targets your back muscles, specifically the latissimus dorsi, and also engages the biceps and shoulders. By performing the movement slowly and with control, you can maximize the benefits and minimize the risk of injury.
One of the key tips for increasing strength and endurance in Pull-up (negative) is to gradually increase the number of repetitions. Start with a comfortable number of repetitions that you can perform with proper form, and then gradually increase the number over time. This progressive overload will stimulate muscle growth and increase your overall strength.
In addition to increasing the number of repetitions, incorporating other exercises that target the muscles used in Pull-up (negative) can also help increase your strength. Exercises such as lat pulldowns, bent-over rows, and inverted rows can be effective in increasing muscle mass and improving your ability to perform Pull-up (negative).
To prevent injury, it's important to warm up properly before starting your Pull-up (negative) workout. This can include dynamic stretches and mobility exercises to prepare your muscles and joints for the movement. Additionally, listening to your body and avoiding excessive strain or overtraining is crucial for injury prevention. Remember to rest and recover adequately between workouts to allow your muscles to repair and grow stronger.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Females Also Perform the Pull-Up (Negative) Exercise?
Yes, females can definitely perform the pull-up (negative) exercise. It's a great way for them to build upper body strength. By incorporating this exercise into their workout routine, females can reap numerous benefits.
It helps to strengthen the back, shoulders, and arms, while also improving overall core stability. Additionally, it can increase muscle definition and improve posture.
What Muscles Are Primarily Targeted During the Pull-Up (Negative) Exercise?
During the pull-up (negative) exercise, the muscles primarily targeted are your back muscles, specifically the latissimus dorsi or lats. This exercise also activates your biceps, forearms, and shoulders.
Incorporating pull-up (negative) into your upper body workout routine can benefit you by strengthening your back, improving posture, and increasing upper body strength.
To progress and increase the difficulty for better muscle gains, you can add weight, perform more reps, or try different variations like wide grip or chin-up grip.
How Often Should I Perform the Pull-Up (Negative) Exercise to See Results?
To see results from the pull-up (negative) exercise, you should perform it regularly. Consistency is key! Aim to do this exercise at least 2-3 times per week.
By doing so, you'll build strength in your upper body, particularly in your back, arms, and shoulders.
Remember to maintain proper form throughout the exercise to maximize its benefits. Practice controlled, slow movements and engage your core muscles for stability.
Are There Any Modifications or Alternatives for Individuals Who Are Unable to Perform a Full Pull-Up (Negative)?
If you can't do a full pull-up (negative), don't worry! There are modifications and alternative exercises available.
For modifications, try using a resistance band to assist you or using a chair to support your feet.
Alternatively, you can try inverted rows, lat pulldowns, or assisted pull-up machines. These exercises target the same muscles as the pull-up (negative) and can help you build strength until you're able to do the full exercise.
Can the Pull-Up (Negative) Exercise Help Improve Grip Strength?
Incorporating negative pull-ups into your grip strength training routine can have several benefits.
It's an effective way to improve your grip strength as you're focusing on the eccentric phase of the exercise, which requires more control and strength.
For beginners, it's important to focus on proper form and technique.
Make sure to lower yourself slowly and in a controlled manner, engaging your grip muscles throughout.
This will help maximize your grip strength gains.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the pull-up (negative) is a highly effective exercise for male athletes looking to build strength and endurance in their upper body.
By maintaining proper form and technique, avoiding common mistakes, and incorporating variations and progressions, athletes can maximize the benefits of this exercise.
With consistent training and a focus on increasing strength, male lifters can improve their performance and reach their fitness goals.

Author
Years ago, the spark of my life’s passion ignited in my mind the moment I stepped into the local gym for the first time. The inaugural bead of perspiration, the initial endeavor, the very first surge of endorphins, and a sense of pride that washed over me post-workout marked the beginning of my deep-seated interest in strength sports, fitness, and sports nutrition. This very curiosity blossomed rapidly into a profound fascination, propelling me to earn a Master’s degree in Physical Education from the Academy of Physical Education in Krakow, followed by a Sports Manager diploma from the Jagiellonian University. My journey of growth led me to gain more specialized qualifications, such as being a certified personal trainer with a focus on sports dietetics, a lifeguard, and an instructor for wellness and corrective gymnastics. Theoretical knowledge paired seamlessly with practical experience, reinforcing my belief that the transformation of individuals under my guidance was also a reflection of my personal growth. This belief holds true even today. Each day, I strive to push the boundaries and explore new realms. These realms gently elevate me to greater heights. The unique combination of passion for my field and the continuous quest for growth fuels my drive to break new ground.