Dumbbell Decline Bench Press (female) – Video Exercise Guide & Tips
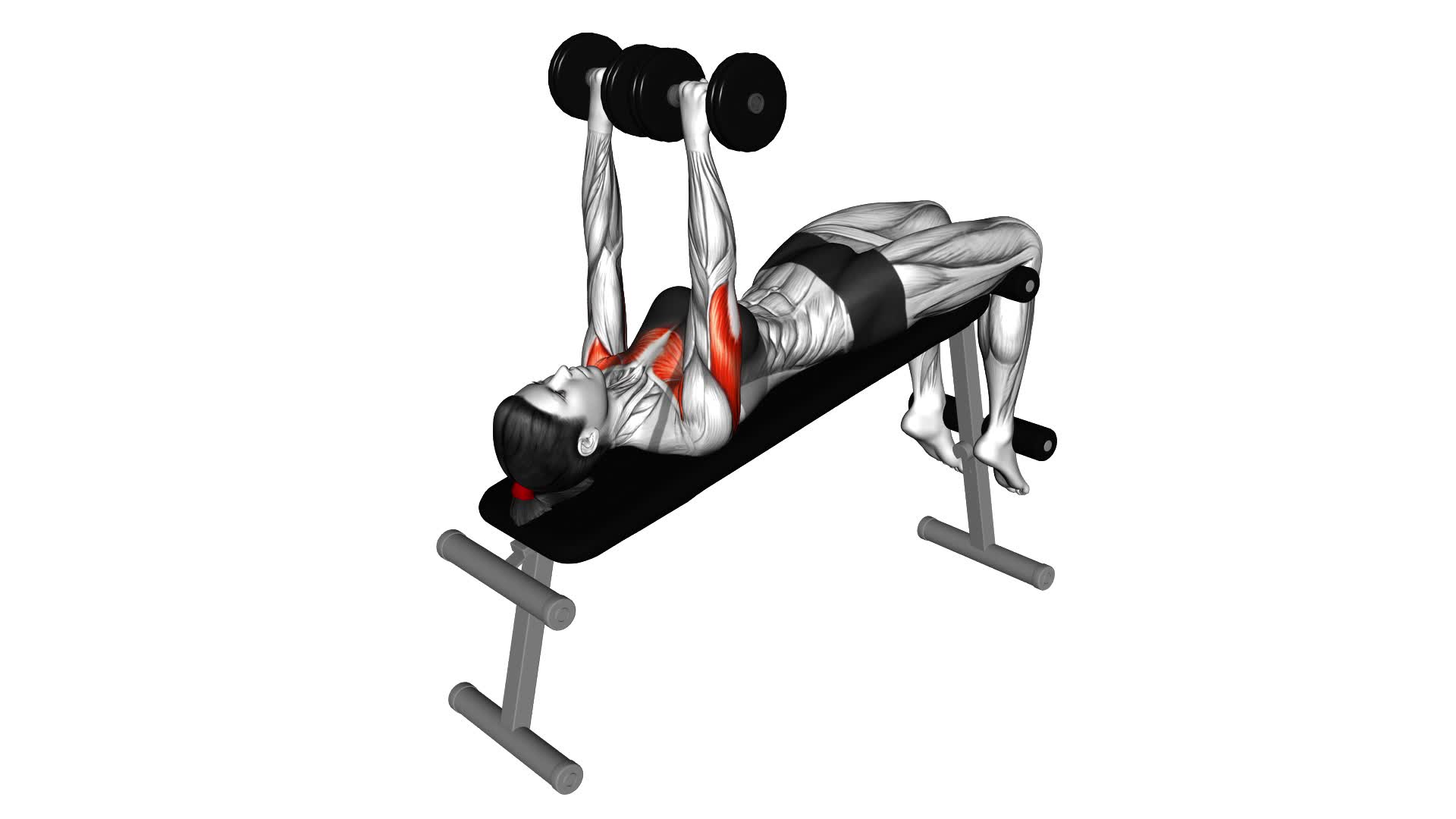
Are you looking to level up your upper body strength and sculpt those muscles? Look no further than the dumbbell decline bench press!
Watch This Exercise Video
This exercise targets your chest, shoulders, and triceps, helping you build a strong and defined upper body.
In this video exercise guide, we'll show you the proper form and technique, recommended weights and sets for beginners, advanced variations, and tips to avoid common mistakes.
Get ready to challenge yourself and achieve your fitness goals!
Key Takeaways
- Targets the lower chest muscles
- Activates the triceps and shoulders
- Improves stability and balance
- Adds variety and challenge to your chest workout
Benefits of the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press
To maximize your workout and target your chest muscles effectively, the dumbbell decline bench press offers numerous benefits. Incorporating decline bench press variations into your workout routine can help you achieve better results.
One of the key benefits of the dumbbell decline bench press is that it specifically targets the lower chest muscles. This exercise involves lying on a decline bench with your feet secured and holding dumbbells in each hand. As you lower the dumbbells towards your chest, your lower chest muscles are engaged, providing a focused and intense workout.
In addition to targeting the lower chest, the dumbbell decline bench press also activates the triceps and shoulders. This compound movement allows you to work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making it an efficient exercise for building overall upper body strength.
Another advantage of incorporating decline bench press variations into your workout is that it helps improve stability and balance. The decline angle of the bench forces you to engage your core muscles to maintain proper form and stability. This not only strengthens your core but also helps prevent injuries during other exercises or daily activities.
Incorporating dumbbell decline bench press into your routine can add variety and challenge to your chest workout. By using different dumbbell weights, angles, or grip positions, you can target different areas of your chest and keep your muscles guessing. This helps prevent plateaus and promotes continuous progress in your fitness journey.
Proper Form and Technique for the Exercise
To perform the dumbbell decline bench press with proper form and technique, it's important to focus on correct body alignment, breathing techniques, and avoiding common mistakes.
Ensure that your body is aligned properly on the bench, with your feet firmly planted on the ground and your back flat against the bench.
Remember to breathe in during the eccentric phase and exhale during the concentric phase, and be mindful of common mistakes such as arching your back or using too much momentum.
Correct Body Alignment
Maintain proper body alignment during the dumbbell decline bench press by ensuring that your back, hips, and feet are all in contact with the bench. This is crucial for effective muscle activation and to avoid strain or injury.
Here's how to achieve correct body positioning:
- Back Alignment:
- Keep your back flat against the bench throughout the exercise.
- Avoid arching or rounding your back, as this can lead to poor form and potential back pain.
- Hip Placement:
- Position your hips firmly on the bench.
- Avoid lifting your hips or allowing them to sag, as this can compromise stability and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Foot Positioning:
- Keep your feet flat on the ground.
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart for optimal stability and balance.
Breathing Techniques
Breathe in sync with your movements to optimize your form and technique during the dumbbell decline bench press. Proper breathing techniques play a crucial role in improving your oxygen intake and overall performance during this exercise.
As you lower the dumbbells towards your chest, inhale deeply through your nose. This allows you to expand your chest and fill your lungs with air.
As you push the dumbbells back up, exhale forcefully through your mouth, engaging your core muscles and enhancing your stability. By coordinating your breathing with each repetition, you ensure a steady flow of oxygen to your muscles, promoting endurance and preventing fatigue.
Now, let's move on to the next section where we'll discuss common mistakes to avoid during the dumbbell decline bench press.
Common Mistakes Avoided
As you continue with the dumbbell decline bench press, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder proper form and technique. To ensure you're performing the exercise correctly, here are some technique tips to keep in mind:
- Grip: Avoid using a grip that's too narrow or too wide. Find a grip that feels comfortable and allows you to maintain control throughout the movement.
- Elbow Position: Keep your elbows tucked in close to your body rather than flaring them out to the sides. This helps to engage your chest muscles more effectively.
- Range of Motion: Lower the dumbbells until your upper arms are parallel to the ground. Going too low can strain your shoulders, while not going low enough will limit the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Breathing: Remember to exhale as you push the dumbbells up and inhale as you lower them down. This helps to stabilize your core and maintain proper form.
Recommended Weight and Sets for Beginners
To get started with the dumbbell decline bench press as a beginner, it's important to choose the proper starting weight. Start with a weight that challenges you but allows you to maintain proper form and complete the recommended number of repetitions.
As you progress, gradually increase the weight to continue challenging your muscles. Aim to perform the exercise 2-3 times per week to allow for adequate rest and recovery.
Proper Starting Weight
How much weight should you start with for the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press as a beginner? It's important to choose the right starting weight to ensure proper form and prevent injury. Here are some guidelines to help you determine the proper weight for your first attempt:
- Start with a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with good form.
- Aim for a weight that you can comfortably complete 8 to 12 repetitions with.
- If the weight feels too easy, increase it gradually in small increments.
- If the weight feels too challenging, decrease it until you can perform the exercise with proper form.
Gradual Weight Progression
Once you have determined the proper starting weight for the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press, you can begin gradually increasing the weight and sets to continue challenging your muscles and promoting growth.
Weight progression is an essential part of any exercise routine, as it helps to continuously challenge your muscles and prevent plateauing. As a beginner, it's important to start with a weight that's manageable and allows you to perform the exercise with proper form. Once you feel comfortable with the weight, you can gradually increase it by 2-5 pounds each week.
Additionally, you can also modify the exercise by increasing the number of sets. For beginners, it's recommended to start with 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions and gradually progress to 3-4 sets as your strength improves.
Remember to listen to your body and make adjustments accordingly to avoid injury and ensure steady progress.
Ideal Set Frequency
To determine the ideal set frequency for beginners in the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press, it's important to consider the recommended weight and sets that will allow for proper muscle development and progression. Here are some guidelines to help you find the right set frequency and workout intensity:
- Start with a weight that challenges you but allows you to maintain proper form throughout the exercise.
- Begin with 2 sets of 8-10 repetitions. This will help you focus on building strength and endurance without overwhelming your muscles.
- As you become more comfortable and stronger, gradually increase the number of sets to 3 or 4 while keeping the repetitions within the 8-10 range.
- Remember to listen to your body and adjust the weight and sets accordingly. It's better to start with a lighter weight and gradually increase it rather than risking injury by using too much weight too soon.
Advanced Variations to Challenge Your Muscles
Try incorporating these five advanced variations into your dumbbell decline bench press routine for an extra challenge and increased muscle engagement.
Advanced modifications can help take your workout to the next level and target specific muscle groups more effectively.
One variation is the alternating decline bench press, where you alternate pressing each dumbbell up while the other one stays lowered. This variation helps improve stability and coordination while challenging your muscles in a different way.
Another variation is the close-grip decline bench press, where you bring your hands closer together on the dumbbells. This targets the triceps more intensely and can help build strength in that area.
Additionally, you can try the decline fly, which involves lowering the dumbbells out to the sides, focusing on the chest muscles.
Another variation is the decline press with a twist, where you rotate your wrists as you press the dumbbells up. This engages the shoulders and core muscles even more.
Lastly, you can incorporate the decline press with a leg raise, where you lift your legs off the ground as you press the dumbbells up. This adds an extra challenge to your core muscles.
Remember to always use proper form and start with lighter weights when attempting these advanced variations.
Tips for Avoiding Common Mistakes During the Exercise
To ensure proper form and maximize the effectiveness of your dumbbell decline bench press, it's important to be aware of common mistakes and take steps to avoid them. By avoiding these mistakes, you can minimize the risk of injuries and maximize your results.
Here are some tips to help you avoid common mistakes during the exercise:
- Maintain proper form:
- Keep your back flat against the bench to avoid straining your lower back.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body throughout the movement.
- Use the correct weight:
- Start with a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form.
- Gradually increase the weight as you get stronger, but avoid using weights that are too heavy and compromise your form.
- Control the movement:
- Lower the dumbbells slowly and under control, maintaining tension in your chest muscles.
- Avoid bouncing the weights off your chest, as this can lead to injuries.
- Focus on breathing:
- Inhale as you lower the dumbbells and exhale as you push them back up.
- Proper breathing technique helps maintain stability and prevents unnecessary strain.
How to Incorporate the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press Into Your Workout Routine
You can incorporate the dumbbell decline bench press into your workout routine by following these steps.
The dumbbell decline bench press is a great exercise that targets the lower chest muscles. To begin, set up a decline bench at a 30-45 degree angle and grab a pair of dumbbells. Lie down on the bench with your feet secured and the dumbbells at shoulder level. Press the dumbbells up, extending your arms fully, and then slowly lower them back down to the starting position. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
To add variety to your routine, you can try different dumbbell decline bench press variations. One option is the alternating dumbbell decline bench press, where you press one arm at a time while the other arm remains extended. This challenges your core stability and adds an element of asymmetrical training. Another variation is the close grip dumbbell decline bench press, where you bring your hands closer together on the dumbbells, targeting the triceps muscles more.
To incorporate the decline bench press into a full body workout, you can include it as one of your pushing exercises. For example, you can pair it with exercises like the dumbbell shoulder press or the push-up to target different muscle groups.
Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as you get stronger. And as always, consult with a professional trainer or coach to ensure you're using proper form and technique.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Do the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press if I Have a Shoulder Injury?
If you have a shoulder injury, it may be best to avoid the dumbbell decline bench press. This exercise puts a significant amount of stress on your shoulders.
However, there are modifications you can make to make it more shoulder-friendly. It's always important to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified trainer for guidance.
Additionally, there are several other chest exercises that are less demanding on the shoulders, such as push-ups or chest presses with resistance bands.
Is It Necessary to Have a Spotter While Performing the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press?
While performing the dumbbell decline bench press, it's important to consider the spotter's importance and maintaining proper form.
Having a spotter can provide an extra level of safety by assisting you in case you struggle with the weights or need help with re-racking them.
Additionally, a spotter can keep an eye on your form and provide feedback to ensure you're performing the exercise correctly.
Can I Use a Flat Bench Instead of a Decline Bench for This Exercise?
Yes, you can use a flat bench instead of a decline bench for this exercise. Using a flat bench will target your chest muscles differently but still effectively.
However, it's important to note that the decline bench specifically targets the lower chest muscles more.
If you don't have access to a decline bench, there are alternative exercises like push-ups, chest dips, or using resistance bands that can also work your chest muscles effectively.
How Often Should I Include the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press in My Workout Routine?
Including the dumbbell decline bench press in your workout routine can be beneficial for targeting your lower chest muscles.
The frequency at which you should include this exercise depends on your overall fitness goals and the intensity of your workouts.
Generally, incorporating the dumbbell decline bench press 1-2 times per week can help you build strength and muscle in your chest.
However, it's important to listen to your body and avoid overtraining to prevent injury.
Are There Any Alternative Exercises That Target the Same Muscles as the Dumbbell Decline Bench Press?
If you're looking for alternative exercises that target the same muscles as the dumbbell decline bench press, there are a few options you can consider.
One option is the decline push-up, which works the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
Another alternative is the cable chest press, which allows you to adjust the resistance and target the chest muscles effectively.
Lastly, you can try the decline dumbbell fly, which focuses on the chest muscles and helps improve upper body strength.
Conclusion
To conclude, the dumbbell decline bench press is an effective exercise for targeting the lower chest muscles. By following proper form and technique, beginners can gradually increase the weight and sets to improve strength and muscle development.
Advanced variations can provide added challenge for those looking to push their limits. Remember to avoid common mistakes and incorporate this exercise into your workout routine for maximum benefits.
Stay consistent and dedicated to achieve your fitness goals.

Author
Years ago, the spark of my life’s passion ignited in my mind the moment I stepped into the local gym for the first time. The inaugural bead of perspiration, the initial endeavor, the very first surge of endorphins, and a sense of pride that washed over me post-workout marked the beginning of my deep-seated interest in strength sports, fitness, and sports nutrition. This very curiosity blossomed rapidly into a profound fascination, propelling me to earn a Master’s degree in Physical Education from the Academy of Physical Education in Krakow, followed by a Sports Manager diploma from the Jagiellonian University. My journey of growth led me to gain more specialized qualifications, such as being a certified personal trainer with a focus on sports dietetics, a lifeguard, and an instructor for wellness and corrective gymnastics. Theoretical knowledge paired seamlessly with practical experience, reinforcing my belief that the transformation of individuals under my guidance was also a reflection of my personal growth. This belief holds true even today. Each day, I strive to push the boundaries and explore new realms. These realms gently elevate me to greater heights. The unique combination of passion for my field and the continuous quest for growth fuels my drive to break new ground.







